Welcome to the future – The Metaverse
The Metaverse is the new iteration of the internet. Although there is also a lot of marketing hype wrapped up around the idea of the metaverse, the truth is that our interaction with one another has changed and will continue to evolve into the unknown. The Metaverse will likely attract scrutiny from governments, parents, ONGs, etc. But it is here to stay, so we need to learn from it, how it works, what it can do, what benefits and dangers it can bring, and how can we invest in it, especially since we are at a very early stage. Cryptos and security (including anti-money laundering), use of decentralized finance (DeFi), crypto assets and NFTs, hardware and software, and intellectual property rights are and will continue to be great sources of startups we need to keep an eye on.
However, in this article we will give a snapshot for those of us who were born before 2010, and who need a hand when it comes to new tech and new ways to interact with each other.

What is the metaverse?
Taking a very simplistic view, it is the combination of immersive experiences including gaming, internet, and continuous social interaction all encompassed by Web 3. Mark Zuckerberg described it as just an enhanced internet (combining 3D, VR/AR, and persistence).
The Metaverse is a conceptualized version of the next generation of the internet that supports a variety of real-time applications across devices. The Metaverse is rapidly emerging as a potential platform for big tech innovations, and has attracted both attention (and investments). It is not easy to define the Metaverse. It’s partly a vision of what the internet might look like in the future, and partly a way of capturing current trends in online infrastructure.
The Metaverse is more than Virtual Reality or Augmented Reality. Much of what happens in the Metaverse can also be accessed through a PC or a mobile phone. Think of Fortnite for example. This can clearly be in the Metaverse. Virtual Reality is not the only thing that the Metaverse offers. Most users will be able to access the internet via their smartphones in the near future. However, VR will be available for a growing number of participants as the consoles become mainstream, cheaper and more available as many hardware manufacturers build on the success of the existing platforms.
Metaverse also has (or may have) deep impact on the digital economy. In the Metaverse people value digital assets more than physical assets. You can broaden that to digital experiences and digital relationships as well. Users can buy, sell, build, and trade goods. In the more idealistic visions of the metaverse, it’s interoperable, allowing you to take virtual items like clothes or cars from one platform to another as everything may be interconnected. Think of it happening as close as possible to the real world. What difference does it make if you buy a suit in the real world for you to wear or if you buy it in the Metaverse? At the end of the day, some people will “see” it in one place and some in the other. If you spend more time in the Metaverse, then why shouldn’t you spend more money there?
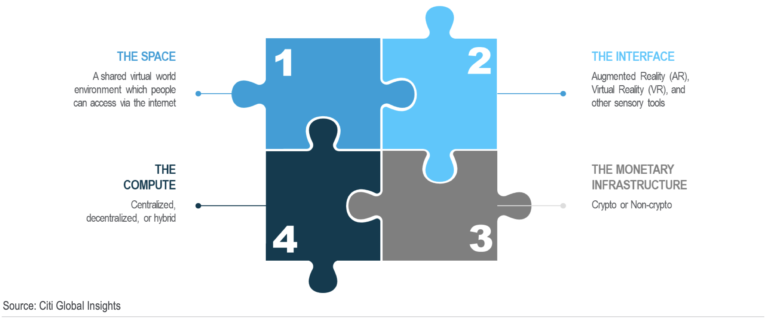
Most platforms have virtual identities, avatars, and inventories that are tied to their own platform. However, we believe that the Metaverse may one day join them all. And you would be able to create a persona that you can take everywhere, just as you walk from one bar to another.
Nowadays it is difficult to separate “games” from “internet” from “VR headsets”. But picture the Metaverse as everything combined, in a place where people do not leave their couches… Or think of the Matrix.
(We have borrowed a useful graph from the Citi report)

What is still needed
This is where angel investors, VCs and the broader investment community will be focusing on the near future. The scalability of the Metaverse is immense, as everything will happen across borders. But the current internet infrastructure is not suitable for building a fully immersive content streaming Metaverse that allows users to seamlessly move from one experience to the next. Platforms are independent and have been built in this way. We expect substantial investment in technology to make the Metaverse vision a reality.
And infrastructure must also be developed. In this sense, we refer not only to VR headsets and faster devices, but also to the broader internet services and speeds. To create a more real user experience, low latency is crucial. This refers to the time it takes for a data signal from one point on a network to travel to another. It is important to reduce latency and provide faster connectivity speeds. Network bandwidth must be increased and delivered, as only a small percentage of the world’s population will have access to 5G in 2025. Today’s network infrastructure is not suitable for creating the Metaverse experience.
Finally, we believe the Metaverse, would encapsulate a range of forms of money, including the existing/traditional kind f money as well as upcoming/digitally-native forms — cryptocurrency, stablecoins, central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) — that not available in a pre-blockchain virtual world. Money as we know it will change, and the Metaverse will be the ideal place to test.
The market size.
A very interesting and comprehensive white paper from Citi puts the target addressable market (TAM) for the Metaverse anywhere from $8 to $13 trillion. Needless to say this is a huge opportunity and a number we shall see quoted in many pitch decks to come in the future. Expert contributors to the Citi White Paper indicate a potential range of users of up to five billion including unique internet users and Virtual Reality/Augmented Reality-device user base.
Applications and use cases
The Metaverse may be the next generation of the internet. It would combine the physical and digital worlds in an immersive manner. The following are just some of the potential use cases of the metaverse. Ideally, one could think that ANYTHING you can do in “real” life can be translated to the virtual world (to a higher or lower degree). The most popular use cases would include:
- Art
- Architecture and design
- Education
- Social Commerce
- Digital Events like concerts, tourism, conferences
- Developer economies
- Smart manufacturing
- Creator economies
- Advertising
- Virtual Communities
- Gaming
- Working communities and spaces
- Healthcare
- Virtual Cities
“You can think about the Metaverse as an embodied internet, where instead of just viewing content, you are in it. And you feel present with other people as if you were in other places, having different experiences that you couldn’t necessarily do on a 2D app or webpage, like dancing, for example, or different types of fitness.”
Mark Zuckerberg, CEO of Meta.
Invest in the future
You can always choose to invest in publicly traded stocks like Meta. However, trying out startups that bring exciting hardware and software concepts to the meta verse will prove better opportunities of bagging higher returns.
We recommend to look for founders with a vision and right skills, and we are committed to bringing you interesting startups that you can consider investing on in the future editions of this newsletter.


